April 2024, Volume 35, Issue 2
The Perils of Propaganda
A review of How to Win an Information War: The Propagandist Who Outwitted Hitler, by Peter Pomerantsev.
April 2024, Volume 35, Issue 2
A review of How to Win an Information War: The Propagandist Who Outwitted Hitler, by Peter Pomerantsev.
January 2024, Volume 35, Issue 1
In East-Central Europe, neither physical proximity nor memories of Soviet domination have united countries in their response to the war in Ukraine. What matters most is who stands to benefit.


July 2023, Volume 34, Issue 3
People obsess over where Russia’s democracy went wrong. The truth is it did not fail: Russia’s democratic transition never got off the starting blocks.


April 2023, Volume 34, Issue 2
Vladimir Putin’s reputation as a skillful leader was buoyed by years of economic good fortune. But when his regime faltered, his rule quickly descended into the fearful, repressive, and paranoid state we see today.


January 2023, Volume 34, Issue 1
When Vladimir Putin launched a massive invasion of Ukraine, he expected an easy victory. Instead, the world has witnessed an object lesson in how a corrupt Russian regime crippled its own military power.

October 2022, Volume 33, Issue 4
Will Russia’s war tip the Kremlin even further toward tyranny while fortifying Ukraine’s democracy? That will depend on Vladimir Putin and Volodymyr Zelensky as much as on the course of the war itself.
July 2022, Volume 33, Issue 3
The more determined democracies are to avoid war, the greater the risk that autocracies will wage it.
July 2022, Volume 33, Issue 3
Why did Russia invade Ukraine? And why are Russian forces fighting so poorly? The internal logic of its personalist dictatorship is to blame.
July 2022, Volume 33, Issue 3
More than window dressing, public-opinion surveys and elections provide a crucial insight into the Russian people’s relationship with their regime.
July 2022, Volume 33, Issue 3
The first two months of the war alone turned the Russian clock back decades, undoing thirty years of post-Soviet economic gains and reducing the country to an international pariah state.


July 2022, Volume 33, Issue 3
The Kremlin wields food as a weapon and a shield against Western interference. But Putin’s push for food autarky could backfire, driving up prices and turning Russians against the regime.


April 2022, Volume 33, Issue 2
Forget his excuses. Russia’s autocrat doesn’t worry about NATO. What terrifies him is the prospect of a flourishing Ukrainian democracy.


October 2021, Volume 32, Issue 4
Thirty years after the Soviet Union collapsed, Russia is firmly in the grip of an autocrat. Where did Russia’s path go wrong?
July 2021, Volume 32, Issue 3
Authoritarian propaganda and manipulation are leading democratic publics to see foreign autocracies as more powerful than they actually are.

July 2021, Volume 32, Issue 3
Is Russia formidable? The answer, two new books argue, lies in the highly centralized inner workings of Putin’s autocracy.


October 2020, Volume 31, Issue 4
Through greater savvy engagement with international law, authoritarians are seeking not only to shield themselves from criticism, but to reshape global norms in their favor.
July 2020, Volume 31, Issue 3
The illiberal credo prominent in Russia’s foreign policy is more than just a clever political ploy. Rather, this outlook reflects the traumatic experience of the 1990s, and it is stoked by young political thinkers, the Russian Orthodox Church, and the Kremlin itself.
January 2020, Volume 31, Issue 1
Lacking any ideas for shoring up Russian society, Putin has settled on picking a fight with Ukraine.

October 2018, Volume 29, Issue 4
Taking advantage of broad global respect for regionalism, authoritarian regimes are using their own regional organizations to bolster fellow autocracies. These groupings offer a mechanism for lending legitimacy, redistributing resources, and insulating members from democratic influences.
January 2018, Volume 29, Issue 1
Russia’s ruling elite have used corruption not only to line their own pockets, but also as a tool of domestic political control and global power projection.

October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
Under Vladimir Putin, Russia’s ruling class again claims to represent a superior alternative to liberal democracy. How can we theorize this regime? Putinism is a form of autocracy that is conservative, populist, and personalistic. Its conservatism means that Putinism prioritizes maintaining the status quo and avoiding instability. Conservatism also overlaps with Putinism’s populism in crowd-pleasing broadsides against gay rights and feminism, but gives…
October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
Read the full essay here. “The pursuit of national glory,” which M. Steven Fish counts among the features of Vladimir Putin’s “populism,” is emerging as central to the regime’s legitimation. Unlike previous instances of patriotic mobilization (around the Second Chechen War and the 2008 Georgia war), the current one appears to have evolved into a…
October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
Read the full essay here. This essay argues that the sources of the current revival of Russian authoritarianism lie in the country’s economic and political history. Among the major factors behind President Putin’s rise and consolidation of power, it cites an ideological overemphasis on the state that fosters hostility toward human rights and liberties; deeply…
October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
Read the full essay here. The Kremlin’s ability to maintain power and popularity despite an aging leader, an ailing economy, a rallying opposition, and many other domestic and international challenges is puzzling given current theories of authoritarianism. These theories focus on some combination of material interests, institutional engineering, and the charisma and skill of the…
October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
Read the full essay here. The Russian system of personalized power is growing ever more dependent on the same strategies that proved useless in sustaining the USSR. While the system still has the potential to limp along, its survival tactics render the it progressively more dysfunctional. Among the circumstances weighing against the system’s survival are…
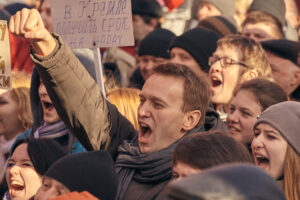

October 2017, Volume 28, Issue 4
More Russians are rejecting the Kremlin’s corruption and authoritarianism. They—and not the regime—are Russia’s future.
January 2016, Volume 27, Issue 1
Although the leading authoritarian regimes are today integrated in many ways into the global system, they have not become more like the democracies; instead, they have been devising policies and practices aimed at blocking democracy’s advance.
January 2016, Volume 27, Issue 1
While “autocracy promotion” presents a real danger, its influence so far has been limited. Because authoritarian regimes are concerned first with furthering their own interests, their interventions often have contradictory effects, sometimes even inadvertently fostering greater pluralism.
October 2015, Volume 26, Issue 4
The Kremlin is now bringing to the rest of the world the kind of propaganda and conspiracy theories it has been churning out at home.

April 2015, Volume 26, Issue 2
Even if Vladimir Putin were to lose his grip on office, the “Russian system” might only wind up exchanging one form of personalized power for another in its endless search for self-perpetuation.
April 2015, Volume 26, Issue 2
A review of Putin’s Kleptocracy: Who Owns Russia? by Karen Dawisha.
January 2015, Volume 26, Issue 1
The system of personalized power that has long ruled Russia now faces a new crisis, and it is trying to avert decay through the reassertion of empire.
July 2014, Volume 25, Issue 3
The regime of Vladimir Putin has been a key driver of the crisis in Ukraine. Under challenge at home for several years now, it turned to Ukraine in part to firm up its own grip on power in Russia.
July 2014, Volume 25, Issue 3
Russia has witnessed a growing rapprochement between some of its nationalists and some of its democrats, but this trend is threatened by divisions over the annexation of Crimea.
July 2013, Volume 24, Issue 3
Today’s Russian protest movement in many ways resembles past civil-rights and civil-resistance efforts in other parts of the world, from its commitment to nonviolence to its key demands—a vote that counts and equality under the law. Listen to the podcast.
July 2013, Volume 24, Issue 3
The Putin regime, having faced its first real challenge in the form of mass protests after the 2011 Duma elections, is responding with a series of laws intended to intimidate its civil society opposition, if not stamp it out altogether.

July 2012, Volume 23, Issue 3
A newly awakened Russia is now asking of series of questions, such as how to transform the current system and who will be the actors to lead the transformation.
July 2012, Volume 23, Issue 3
Although they have quieted down as quickly as they flared up, the clamorous protests that followed the dishonest Russian legislative elections in December 2011 have essentially destroyed Putin’s regime, the infamous “managed democracy.”
July 2012, Volume 23, Issue 3
One of the most striking and unexpected features of the recent demonstrations in Russia was the partnership of liberals and nationalists in the ranks of the protesters.
July 2012, Volume 23, Issue 3
After the December 2011 State Duma elections, the Russian opposition and civil society quickly launched large protest rallies in response to electoral fraud.
July 2012, Volume 23, Issue 3
The recent protests in Russia raise the question of whether the Putin regime could fall to a “color” or electoral revolution like those that have ousted other autocratic regimes in postcommunist Europe and Eurasia over the past decade and a half.

April 2011, Volume 22, Issue 2
Why are the unfree regimes of the former Soviet world proving so durable? A lack of ideology and—perhaps surprisingly—a degree of openness are proving to be not so much problems for authoritarianism as bulwarks of it.
January 2011, Volume 22, Issue 1
A review of Lonely Power: Why Russia Has Failed to Become the West and the West Is Weary of Russia by Lilia Shevtsova.
January 2010, Volume 21, Issue 1
The author analyses the confluence of several elements that helped to set Russia’s course: the influence of history; the challenges of the transformation process itself; the importance of leadership; and the role of the West.

April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
There is no consensus about the nature of the political system in Moscow today. Yet how one understands the motivations propelling Russian policy abroad depends on how one understands its regime at home.
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
A fan of Mario Puzo’s Godfather novels will see the Putin government for what it is: a mafia.
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. Arguably a flawed democracy in the 1990s, Russia took a distinctly authoritarian turn under President Vladimir Putin from 2000 to 2008. The country now lives under a façade democracy that barely conceals the political and administrative dominance of a self-interested bureaucratic corporation. The regime manufactures consent by means of three…
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. Twenty years ago, there was a more thoroughgoing political pluralism in Russia than there is today. In some respects, the forms of democracy-including party consolidation-have been enhanced, but they have been so manipulated as to deprive them of substance. Either “electoral authoritarianism” of “multiparty authoritarianism” (Juan Linz’s terms) may reasonably…
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. The corporatist kleptocracy being erected by Russian President Vladimir Putin is profoundly misunderstood in the West. This model dooms Russia to economic degradation and margin-alization. The current global crisis has made this truth painfully clear. The artificially created image of a threatening West (and U.S. in particular) is now becoming…
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. Of all of the national republics that emerged out of the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia has had the most profound difficulties in determining its national identity. What is the essence of being Russian, and where are the boundaries of the “Russian World”? There has never been a Russian…
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. In contrast to authoritarian power structures, which rest on a form of bureaucratic corporatism that makes the leader its hostage, the regime in Moscow rests on personalized power, something that signals a return to the traditional Russian political matrix. The regime has fused power and property in a manner that…
April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Read the full essay here. The regime in Moscow mixes key features of a capitalist economy with a political system wherein power is monopolized by a close-knit professional and age cohort whose members often have a background in the secret police. Instead of seeking to base its legitimacy on broad-based, transpersonal institutions with character and…

April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
Since Vladimir Putin’s rise to power at the end of the 1990s, siloviki—the people who work for, or used to work for, Russia’s “ministries of force” have spread to posts throughout all the branches of power in Russia.

April 2009, Volume 20, Issue 2
The image of Putin’s Russia as an authoritarian oil state attracts many Western analysts because it seems to carry a promise that falling oil prices will bring regime change. Thus, many were convinced that a major economic crisis would force the Kremlin either to open up the system and allow more pluralism and competition, or…

April 2008, Volume 19, Issue 2
Just as Russia's leaders pretend that they are ruling over a democracy, they also pretend that they are ruling over an empire.
January 2008, Volume 19, Issue 1
The history of twentieth-century European communist parties shows that extremists can be moderated by robust democratic institutions. Without them, however, the inclusion of extremist parties may undermine democracy.

April 2007, Volume 18, Issue 2
The Putin regime is plunging Russia into a deepening crisis. It is time to end the fiction that today's Russia is a democracy.

April 2007, Volume 18, Issue 2
There is a future for democracy in Russia, but it may have to wait until the people begin to feel the problems created by the current system.

April 2007, Volume 18, Issue 2
The Kremlin's ultimate need for democratic legitimacy, both at home and abroad, may be the key vulnerability of the Putin regime.

January 2007, Volume 18, Issue 1
The recent "color revolutions" in the former Soviet Union should lead us to reassess the idea of revolution and also to consider the weaknesses of the concept of "democratic transition.
July 2006, Volume 17, Issue 3
Much like other institutions in post-Soviet Russia, the intelligence and security services have yet to make a transition to real democratic control, and remain infused with the authoritarian tendencies of their Soviet predecessors.
April 2006, Volume 17, Issue 2
There was nothing inevitable about the unraveling of Soviet communism. The role played by individuals such as Aleksandr Yakovlev was crucial.

April 2006, Volume 17, Issue 2
Authoritarians are stepping up their offensive against democracy promotion, and democracy-assistance organizations will have to meet the challenge.

April 2006, Volume 17, Issue 2
From Putin's Russia to Chávez's Venezuela, regimes that claim to be democracies but act like autocracies are emerging as a major long-term threat to freedom.

January 2006, Volume 17, Issue 1
Evidence from the postcommunist countries shows that the strength of the legislature may be the institutional key to democratic consolidation.
January 2006, Volume 17, Issue 1
Vladimir Putin has pulled the plug on democracy in Russia in an effort to strengthen the authority of the central state. But a look at Russian federal relations shows that the state is growing weaker rather than stronger.
July 2005, Volume 16, Issue 3
At the end of the Cold War, semipresidentialism became the modal constitution of the postcommunist world. In Russia and other post-Soviet states, however, this system of government has impeded consolidation.
January 2005, Volume 16, Issue 1
Modest progress in the muslim-majority countries is complemented by mass mobilization for democracy and freedom in Ukraine. Meanwhile, Russia ranks as Not Free for the first time since the fall of communism.
July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
President Vladimir Putin's lopsided election victory was assisted by an unlevel electoral playing field, but elections still matter in Russia and they will make more difficult the consolidation of authoritarianism.

July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
Post-Soviet Russia's future may well turn on the interplay of state power with the business interests that now form Russia's best hope for advances in political pluralism.
July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
The first flush of democratic hopes has faded, as the recent elections have emphasized. But the democratic idea has a foothold, and the presidential machine that swept those elections will not have an easy time retaining its sway.
July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
Russia's liberal-democratic parties have failed. It is time for a new movement that can gain the trust of the Russian people by putting forward a full reform program based on liberal and democratic principles.
July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
Hopes for democratization now rest on the shoulders of the young. Who are they, what do they believe, and what are their political leanings? Survey data offer some clues.
July 2004, Volume 15, Issue 3
Vladimir Putin aspires to be a classic authoritarian modernizer, but in today's globalized world Russia faces challenges that bureaucratic centralization and a traditional strong hand cannot meet.
January 2004, Volume 15, Issue 1
A review of Popular Choice and Managed Democracy: The Russian Elections of 1999 and 2000 by Timothy J. Colton and Michael McFaul; Darkness at Dawn: The Rise of the Russian Criminal State by David Satter; and Putin's Russia by Lilia Shevtsova.
July 2002, Volume 13, Issue 3
A review of Russia’s Unfinished Revolution: Political Change from Gorbachev to Putin, by Michael McFaul.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
The 15 states of the former Soviet fall into three broad categories, largely defined by fault lines of history and culture.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
To grasp what is happening in the former USSR, we must examine the types of nationalism that flourish there.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
Except for the Baltic states, the countries of the former Soviet Union may be less democratic today than in the last years of the USSR.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
The failures of post-Soviet reform notwithstanding, serious strides have been made toward economic and political transformation.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
In the southern reaches of what was once the USSR, democracy seems far off. Can that change?
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
In Russia, formally democratic institutions coexist uneasily with the reality of tightly consolidated bureaucratic and executive power.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
Although his methods are hardly democratic, Putin’s efforts to strengthen the Russian state may help democracy in the long term.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
A leading Russian oppositionist speaks out against continuing official assaults on self-government and human rights.
October 2001, Volume 12, Issue 4
Despite huge changes, the events of the last ten years raise doubts about the notion of “democratic transition” itself.
April 2001, Volume 12, Issue 2
July 2000, Volume 11, Issue 3
Does the election of Vladimir Putin as Russia’s president represent a fundamental turn away from democracy or merely a temporary setback? Although Putin’s apparent indifference to democracy is worrisome, it would be premature to conclude that democracy is lost in Russia.
July 2000, Volume 11, Issue 3
Vladimir Putin soon must make a fundamental choice: whether to hold on to monolithic power or to adopt a reformist course that could leave him at the center of a battle without any guarantee of success.
July 2000, Volume 11, Issue 3
The debate over Russia’s likely course of development under Putin has paid surprisingly little attention to his openly stated goal of reintegrating Russia with other former Soviet republics.
January 2000, Volume 11, Issue 1
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
April 1999, Volume 10, Issue 2
January 1999, Volume 10, Issue 1
On the evening of 20 November 1998, Galina Vasilievna Starovoitova was shot to death outside her St. Petersburg apartment. She was the sixth member of the Russian Duma to have been murdered since that body’s creation in 1993. Most observers agree that this was a political assassination. Starovoitova was a tireless, persistent voice for freedom,…